Product Description
TPED/CE/EN/ISO/DOT/BV/SGS 2L/5L/7L/8L/10L/14L/20L small portable seamless steel gas cylinders filled with oxygen gas,co2 gas, argon gas,helium gas,mixture gas.etc.
| Type | (mm) Outside Diameter |
(L) Water Capacity |
(mm) () Height (Withoutvalve) |
(Kg) (,) Weight(Without valve,cap) |
(Mpa) Working Pressure |
(mm) Design Wall Thickness |
Material Grades |
| ISO102-1.8-150 | 102 | 1.8 | 325 | 3.5 | 150 | 3 | 37Mn |
| ISO102-3-150 | 3 | 498 | 5.2 | ||||
| ISO102-3.4-150 | 3.4 | 555 | 5.7 | ||||
| ISO102-4.4-150 | 4.4 | 700 | 7.2 | ||||
| ISO108-1.4-150 | 108 | 1.4 | 240 | 2.9 | 150 | 3.2 | 37Mn |
| ISO108-1.8-150 | 1.8 | 285 | 3.3 | ||||
| ISO108-2-150 | 2 | 310 | 3.6 | ||||
| ISO108-3-150 | 3 | 437 | 4.9 | ||||
| ISO108-3.6-150 | 3.6 | 515 | 5.7 | ||||
| ISO108-4-150 | 4 | 565 | 6.2 | ||||
| ISO108-5-150 | 5 | 692 | 7.5 | ||||
| ISO140-3.4-150 | 140 | 3.4 | 321 | 5.8 | 150 | 4.1 | 37Mn |
| ISO140-4-150 | 4 | 365 | 6.4 | ||||
| ISO140-5-150 | 5 | 440 | 7.6 | ||||
| ISO140-6-150 | 6 | 515 | 8.8 | ||||
| ISO140-6.3-150 | 6.3 | 545 | 9.2 | ||||
| ISO140-6.7-150 | 6.7 | 567 | 9.5 | ||||
| ISO140-7-150 | 7 | 595 | 9.9 | ||||
| ISO140-7.5-150 | 7.5 | 632 | 10.5 | ||||
| ISO140-8-150 | 8 | 665 | 11 | ||||
| ISO140-9-150 | 9 | 745 | 12.2 | ||||
| ISO140-10-150 | 10 | 830 | 13.5 | ||||
| ISO140-11-150 | 11 | 885 | 14.3 | ||||
| ISO140-13.4-150 | 13.4 | 1070 | 17.1 | ||||
| ISO140-14-150 | 14 | 1115 | 17.7 | ||||
| ISO159-7-150 | 159 | 7 | 495 | 9.8 | 150 | 4.7 | 37Mn |
| ISO159-8-150 | 8 | 554 | 10.8 | ||||
| ISO159-9-150 | 9 | 610 | 11.7 | ||||
| ISO159-10-150 | 10 | 665 | 12.7 | ||||
| ISO159-11-150 | 11 | 722 | 13.7 | ||||
| ISO159-12-150 | 12 | 790 | 14.8 | ||||
| ISO159-12.5-150 | 12.5 | 802 | 15 | ||||
| ISO159-13-150 | 13 | 833 | 15.6 | ||||
| ISO159-13.4-150 | 13.4 | 855 | 16 | ||||
| ISO159-13.7-150 | 13.7 | 878 | 16.3 | ||||
| ISO159-14-150 | 14 | 890 | 16.5 | ||||
| ISO159-15-150 | 15 | 945 | 17.5 | ||||
| ISO159-16-150 | 16 | 1000 | 18.4 | ||||
| ISO180-8-150 | 180 | 8 | 480 | 13.8 | 150 | 5.3 | 37Mn |
| ISO180-10-150 | 10 | 570 | 16.1 | ||||
| ISO180-12-150 | 12 | 660 | 18.3 | ||||
| ISO180-15-150 | 15 | 790 | 21.6 | ||||
| ISO180-20-150 | 20 | 1015 | 27.2 | ||||
| ISO180-21-150 | 21 | 1061 | 28.3 | ||||
| ISO180-21.6-150 | 21.6 | 1087 | 29 | ||||
| ISO180-22.3-150 | 22.3 | 1100 | 29.4 | ||||
| ISO219-20-150 | 219 | 20 | 705 | 27.8 | 150 | 6.1 | 37Mn |
| ISO219-25-150 | 25 | 855 | 32.8 | ||||
| ISO219-27-150 | 27 | 915 | 34.8 | ||||
| ISO219-36-150 | 36 | 1185 | 43.9 | ||||
| ISO219-38-150 | 38 | 1245 | 45.9 | ||||
| ISO219-40-150 | 40 | 1305 | 47.8 | ||||
| ISO219-45-150 | 45 | 1455 | 52.9 | ||||
| ISO219-46.7-150 | 46.7 | 1505 | 54.6 | ||||
| ISO219-50-150 | 50 | 1605 | 57.9 |
| RECORD OF HYDROSTATIC TESTS ON CYLINDERS Time≥ 60S | ||||||||
| S.N | Serial No. | The weight without valve&cap(kg) | Volumetric Capacity(L) | Total expansion(ml) | Permanent expansion(ml) | Percent of Permanent to totalexpanison(%) | Test Pressure 250Bar | Lot and Batch No. |
| 1 | 20S049001 | 13.7 | 10.3 | 76.8 | 1 | 1.3 | 25 | S05 |
| 2 | 20S049002 | 13.7 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 25 | S05 |
| 3 | 20S049003 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 76.0 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 25 | S05 |
| 4 | 20S049004 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 78.0 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 25 | S05 |
| 5 | 20S049005 | 14 | 10.2 | 77.0 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 25 | S05 |
| 6 | 20S049006 | 14.3 | 10.2 | 77.0 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 25 | S05 |
| 7 | 20S049007 | 13.8 | 10.3 | 77.8 | 1 | 1.3 | 25 | S05 |
| 8 | 20S049008 | 14 | 10.2 | 76.0 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 25 | S05 |
| 9 | 20S049009 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 78.0 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 25 | S05 |
| 10 | 20S049571 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 76.0 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 25 | S05 |
| 11 | 20S049011 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 79.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 25 | S05 |
| 12 | 20S049012 | 13.9 | 10.1 | 78.1 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
| 13 | 20S049013 | 14 | 10.2 | 78.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
| 14 | 20S049014 | 13.9 | 10.1 | 79.1 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 25 | S05 |
| 15 | 20S049015 | 14 | 10.2 | 77.0 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 25 | S05 |
| 16 | 20S049016 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 77.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
| 17 | 20S049017 | 14 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 25 | S05 |
| 18 | 20S049018 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 76.0 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 25 | S05 |
| 19 | 20S049019 | 13.8 | 10.2 | 78.0 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 25 | S05 |
| 20 | 20S049571 | 14 | 10.2 | 76.0 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 25 | S05 |
| 21 | 20S049571 | 14 | 10.2 | 79.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 25 | S05 |
| 22 | 20S049571 | 14 | 10.2 | 78.0 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 25 | S05 |
| 23 | 20S049571 | 13.9 | 10.3 | 78.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 25 | S05 |
| 24 | 20S049571 | 14 | 10.2 | 79.9 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
| 25 | 20S049571 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 79.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 25 | S05 |
| 26 | 20S049026 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 78.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
| 27 | 20S049571 | 14 | 10.2 | 77.0 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 25 | S05 |
| 28 | 20S049571 | 14 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 1 | 1.3 | 25 | S05 |
| 29 | 20S049571 | 14 | 10.3 | 75.8 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 25 | S05 |
| 30 | 20S049030 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
| 31 | 20S049031 | 13.9 | 10.1 | 79.1 | 1 | 1.3 | 25 | S05 |
| 32 | 20S049032 | 14 | 10.3 | 76.8 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 25 | S05 |
| 33 | 20S049033 | 14 | 10.2 | 76.0 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 25 | S05 |
| 34 | 20S049034 | 14 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 25 | S05 |
| 35 | 20S049035 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 79.9 | 1 | 1.3 | 25 | S05 |
| 36 | 20S049036 | 14 | 10.3 | 76.8 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 25 | S05 |
| 37 | 20S049037 | 13.8 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 25 | S05 |
| 38 | 20S049038 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 77.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
| 39 | 20S049039 | 13.8 | 10.2 | 78.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
| 40 | 20S049040 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 1 | 1.3 | 25 | S05 |
| 41 | 20S049041 | 14 | 10.2 | 78.0 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 25 | S05 |
| 42 | 20S049042 | 14.2 | 10.1 | 81.1 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 25 | S05 |
| 43 | 20S049043 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 25 | S05 |
| 44 | 20S049044 | 13.9 | 10.1 | 81.1 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
| 45 | 20S049045 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 25 | S05 |
| 46 | 20S049046 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 78.9 | 1 | 1.3 | 25 | S05 |
| 47 | 20S049047 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 79.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 25 | S05 |
| 48 | 20S049048 | 13.9 | 10.1 | 81.1 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 25 | S05 |
| 49 | 20S049049 | 13.6 | 10.4 | 75.7 | 1 | 1.3 | 25 | S05 |
| 50 | 20S049050 | 13.9 | 10.1 | 77.1 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 25 | S05 |
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Steel |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Oxygen Gas and Nitrogen Cylinder |
| Structure: | Gas – Liquid Damping Cylinder |
| Power: | Hydraulic |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Pressure Direction: | Single-acting Cylinder |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can hydraulic cylinders be adapted for specialized applications like material handling?
Yes, hydraulic cylinders can be effectively adapted for specialized applications such as material handling. The versatility, power, and precise control offered by hydraulic cylinders make them well-suited for a wide range of material handling tasks. Hydraulic systems, including cylinders, are commonly used in industrial settings to lift, position, push, pull, and manipulate various types of materials. Here’s a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders can be adapted for specialized material handling applications:
1. Lifting and Lowering:
– Hydraulic cylinders are commonly used for lifting and lowering heavy loads in material handling applications. By utilizing the force generated by hydraulic pressure, cylinders can provide the necessary power to lift and hold loads at different elevations. The precise control offered by hydraulic systems allows for accurate positioning of materials, ensuring efficient and safe lifting operations.
2. Pushing and Pulling:
– Hydraulic cylinders are capable of generating substantial pushing and pulling forces, making them ideal for applications that involve moving or manipulating materials. They can be used to push or pull heavy objects, control the movement of conveyors or rollers, or engage mechanisms for material transfer. The ability to exert high forces with precise control enables hydraulic cylinders to efficiently handle a variety of material handling tasks.
3. Tilting and Rotating:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be adapted to provide tilting and rotating functions in material handling equipment. By integrating cylinders into the design, equipment such as forklifts, cranes, or material handling arms can tilt or rotate to facilitate material placement or maneuvering. Hydraulic cylinders offer the required force and control to achieve smooth and controlled tilting or rotating motions, enhancing operational efficiency in material handling processes.
4. Gripping and Clamping:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be utilized to provide gripping and clamping functions for secure material handling. By incorporating specialized gripping or clamping mechanisms with hydraulic actuation, materials of various shapes and sizes can be securely held or clamped during transportation or processing. Hydraulic cylinders enable precise and adjustable gripping or clamping forces, ensuring the safe and reliable handling of materials.
5. Material Compaction and Forming:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be adapted for material compaction and forming applications. For example, in the production of bricks, hydraulic cylinders are used to apply high pressure and force to compact the raw materials into desired shapes. Similarly, in metal forming processes, hydraulic cylinders are employed to exert force on metal sheets or components, enabling precise shaping and forming operations.
6. Conveyor and Sorting Systems:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be integrated into conveyor and sorting systems to facilitate material movement and sorting. By incorporating hydraulic actuators, conveyor belts or sorting mechanisms can be efficiently controlled for optimal material flow and distribution. Hydraulic cylinders provide the necessary force and control to handle varying load capacities and adjust the speed and position of material transfer, improving the overall efficiency of handling and sorting operations.
7. Customized Designs:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be customized and adapted to meet specific requirements of specialized material handling applications. Engineers can design cylinders with unique dimensions, stroke lengths, mounting options, and sealing arrangements to fit into equipment or systems with specific space limitations or operating conditions. Customized hydraulic cylinders ensure optimal performance and compatibility for specialized material handling tasks.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders can be effectively adapted for specialized material handling applications, offering the necessary force, control, and versatility required in various material handling tasks. Whether it involves lifting and lowering, pushing and pulling, tilting and rotating, gripping and clamping, material compaction and forming, or integration into conveyor and sorting systems, hydraulic cylinders provide reliable and efficient solutions. Their adaptability, precise control, and ability to handle heavy loads make hydraulic cylinders a valuable component in optimizing material handling processes across different industries.

Contribution of Hydraulic Cylinders to the Precision of Robotic and Automation Systems
Hydraulic cylinders play a significant role in enhancing the precision of robotic and automation systems. These systems rely on precise and controlled movements to perform various tasks with accuracy and repeatability. Let’s explore how hydraulic cylinders contribute to the precision of robotic and automation systems:
- Precise Positioning: Hydraulic cylinders enable precise positioning of robotic arms or automation components. They provide accurate control over the linear motion required for tasks such as picking, placing, and assembly. By precisely controlling the extension and retraction of the hydraulic cylinder, the system can achieve the desired position with high accuracy, ensuring precise alignment and consistent results.
- Controlled Motion: Hydraulic cylinders offer controlled and smooth motion, which is crucial for precise operation in robotic and automation systems. The flow of hydraulic fluid can be precisely regulated to control the speed and acceleration of the cylinder’s movement. This precise control allows for gentle and controlled movements, minimizing vibrations, overshooting, or jerky motions that could affect the accuracy of the system.
- Force Control: Hydraulic cylinders provide force control capabilities that contribute to precision in robotic and automation systems. By adjusting the hydraulic pressure, the force exerted by the cylinder can be precisely controlled. This is particularly valuable in applications that require delicate force-sensitive tasks, such as gripping fragile objects or performing precise force feedback during assembly or testing processes.
- Load Handling: Hydraulic cylinders are capable of handling heavy loads, allowing robotic and automation systems to manipulate and transport objects with precision. The high force capabilities of hydraulic cylinders ensure secure and stable handling of loads, minimizing the risk of slippage or imprecise positioning. This is crucial in applications where precise control over heavy objects is required, such as material handling or industrial assembly processes.
- Durability and Reliability: Hydraulic cylinders are known for their durability and reliability in demanding industrial environments. The ability to withstand repeated use, high loads, and harsh conditions ensures consistent performance over time. This reliability contributes to the precision of robotic and automation systems, as any deviation or failure in the cylinder’s movement could lead to inaccuracies or disruptions in the system’s operation.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders make significant contributions to the precision of robotic and automation systems by enabling precise positioning, controlled motion, force control, load handling, and offering durability and reliability. These capabilities ensure accurate and repeatable movements, minimize errors, and enhance the overall precision of the system. By incorporating hydraulic cylinders into robotic and automation systems, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of precision, efficiency, and productivity in various industrial applications.

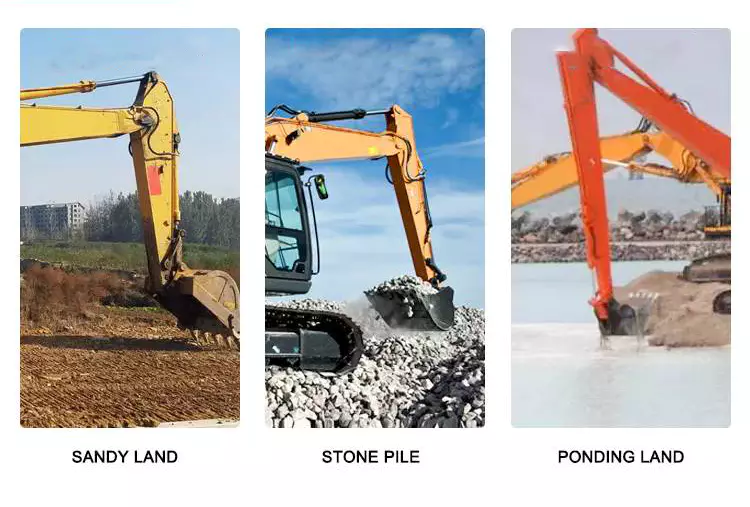
What factors should be considered when selecting the right hydraulic cylinder for an application?
When selecting the right hydraulic cylinder for an application, several important factors need to be considered. These factors help ensure that the chosen hydraulic cylinder is suitable for the specific requirements of the application and will perform reliably. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Load Requirements:
– One of the crucial factors to consider is the load requirement of the application. Determine the maximum load that the hydraulic cylinder needs to handle. Consider both the static load (when the cylinder is stationary) and the dynamic load (when the cylinder is in motion). The load requirement will impact the cylinder’s bore size, rod diameter, and overall strength. Choose a hydraulic cylinder with a load capacity that exceeds the application’s maximum load to ensure safety and longevity.
2. Stroke Length:
– The stroke length refers to the distance the hydraulic cylinder needs to extend and retract to perform the desired motion. Measure the required stroke length based on the application’s operational requirements. It is essential to choose a hydraulic cylinder with a stroke length that matches or exceeds the required distance. Consider any potential variations or adjustments in the stroke length that may be needed in the future.
3. Operating Pressure:
– Consider the operating pressure required for the application. The hydraulic cylinder must be capable of withstanding the maximum pressure within the hydraulic system. Ensure that the selected cylinder has a pressure rating that exceeds the application’s maximum operating pressure. This ensures safety and prevents premature failure.
4. Speed Requirements:
– Determine the required speed of the hydraulic cylinder’s movement for the application. Consider both the extension and retraction speeds. Select a cylinder that can achieve the desired speed while maintaining precise control and stability. It is important to choose a cylinder that can handle the required speed without compromising performance or safety.
5. Mounting:
– Evaluate the available space and mounting requirements for the hydraulic cylinder. Consider the mounting type (such as flange, foot, trunnion, or clevis), the available mounting points, and any specific mounting constraints. Ensure that the selected cylinder can be easily and securely mounted in the desired location.
6. Environmental Factors:
– Assess the environmental conditions in which the hydraulic cylinder will operate. Consider factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, exposure to chemicals, dust, or corrosive substances. Choose a cylinder that is designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions of the application. This may involve selecting appropriate materials, coatings, or seals to ensure the longevity and performance of the cylinder.
7. Cylinder Configuration:
– Determine the appropriate cylinder configuration based on the application’s requirements. Consider factors such as single-acting or double-acting cylinders, telescopic cylinders for limited space, or custom configurations for unique applications. Evaluate the specific needs of the application to select the most suitable cylinder configuration.
8. Maintenance and Serviceability:
– Consider the maintenance and service requirements of the hydraulic cylinder. Evaluate factors such as ease of access for maintenance, availability of spare parts, and the reputation of the manufacturer or supplier in terms of customer support and after-sales service. Choosing a reliable and reputable brand can ensure ongoing support and availability of spare parts when needed.
9. Compliance and Standards:
– Depending on the industry and application, certain compliance standards may need to be met. Consider any industry-specific regulations, safety standards, or certifications that the hydraulic cylinder should comply with. Ensure that the selected cylinder meets the required standards and certifications for the application.
10. Cost and Budget:
– Finally, consider the cost and budget for the hydraulic cylinder. While it is important to select a cylinder that meets the application’s requirements, it is also necessary to consider the overall cost-effectiveness. Evaluate the initial purchase cost, long-term maintenance costs, and the expected lifespan of the cylinder. Balancing the cost and quality will help in selecting a hydraulic cylinder that provides the best value for the application.
By considering these factors in the selection process, it becomes possible to choose the right hydraulic cylinder that meets the specific requirements of the application in terms of load capacity, stroke length, operating pressure, speed, mounting, environmental conditions, maintenance needs, compliance, and cost-effectiveness. Proper selection ensures optimal performance, reliability, and longevity of the hydraulic cylinder in the intended application.

editor by CX 2023-12-17
China Best Sales Factory Direct Sale Reasonable Price Oxygen Gas Cylinder vacuum pump ac
Product Description
Factory Direct Sale Reasonable Price Oxygen Gas Cylinder
1.Product Description
The industrial cylinders are all made by high quality seamless steel pipe,consistent height, smoothly painting, and excellent properties, which is widely used for steel cutting, welding, electronic, medical and other fields.and are supposed to be used repeatedly for keeping argon which is mainly used for steel cutting, welding, electronic, medical and so on.
| Outside diameter(mm) | 203 |
| Water capacity(L) | 15 |
| Height(mm) | 790 |
| Weight(kg) | 21.6 |
| Design wall thickness(mm) | 5.3 |
| Working Pressure(Mpa) | 15 |
| Test pressure(Mpa) | 25 |
| Material | 37Mn |
| Head Protection | Tulip Cap or Common Cap |
| Cylinder Color | As Clients Require |
| Certification Provided | ISO9809/TPED/DOT |
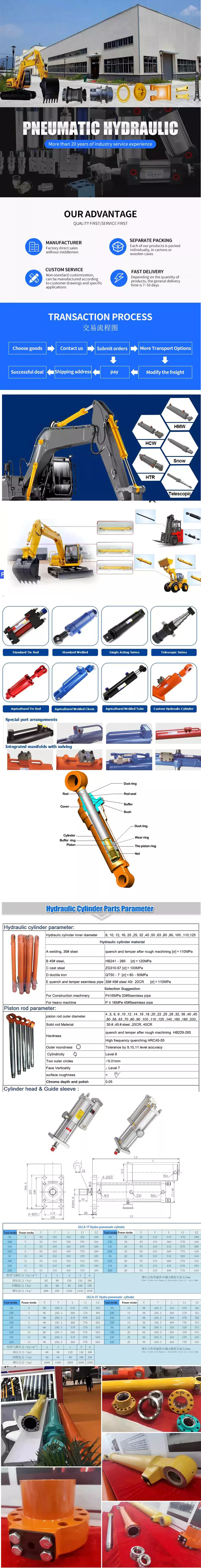
2.Gas Cylinder Process
3.Company Profile
Located in ZheJiang , SEFIC is a professional supplier of gas and gas equipment. Founded in the 90s, the company has already accumulated enough experience and became 1 of the best suppliers of all kinds of gas and gas equipment. Besides, it is 1 of the earliest in the country to gain the License of Pressure Vessel Type A2 and C2, ISO9
| Material: | Steel |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Gas Storage |
| Structure: | General Cylinder |
| Power: | Hydraulic |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Pressure Direction: | Double-acting Cylinder |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
How do hydraulic cylinders handle variations in temperature and harsh operating environments?
Hydraulic cylinders are designed to handle variations in temperature and harsh operating environments by incorporating specific features and materials that ensure their durability, reliability, and performance. The ability of hydraulic cylinders to withstand extreme temperatures, corrosive environments, and other harsh conditions is crucial for their successful operation in a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders handle variations in temperature and harsh operating environments:
1. Temperature Range:
– Hydraulic cylinders are designed to operate within a specified temperature range. The materials used in their construction, such as cylinder barrels, pistons, seals, and lubricants, are selected to withstand the anticipated temperature variations. Specialized seals and O-rings made from materials like nitrile, Viton, or polyurethane are used to maintain their sealing properties over a wide temperature range. Heat-resistant coatings or thermal insulation may be applied to certain components to protect them from high temperatures.
2. Thermal Expansion:
– Hydraulic cylinders are designed to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction that occurs with temperature changes. The materials used in their construction have different coefficients of thermal expansion, allowing the cylinder components to expand or contract at a similar rate. This design consideration prevents excessive stress, binding, or leakage that could result from thermal expansion or contraction.
3. Heat Dissipation:
– In applications where hydraulic cylinders are subjected to high temperatures, heat dissipation mechanisms are employed to prevent overheating. Cooling fins or heat sinks may be incorporated into the cylinder design to increase the surface area for heat transfer. In some cases, external cooling methods such as air or liquid cooling systems can be used to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
4. Corrosion Resistance:
– Hydraulic cylinders used in harsh operating environments are constructed from materials that exhibit excellent corrosion resistance. Stainless steel, chrome-plated steel, or other corrosion-resistant alloys are commonly used for cylinder components exposed to corrosive substances or environments. Additionally, surface treatments such as coatings, plating, or specialized paints can provide an extra layer of protection against corrosion.
5. Sealing Systems:
– Hydraulic cylinders employ sealing systems that are specifically designed to withstand harsh operating environments. The seals used in hydraulic cylinders are selected based on their resistance to temperature extremes, chemicals, abrasion, and other environmental factors. Specialized seal designs, such as wiper seals, rod seals, or high-temperature seals, are utilized to maintain effective sealing and prevent contamination of the hydraulic fluid.
6. Lubrication:
– Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of hydraulic cylinders, particularly in harsh operating environments. Lubricants are selected based on their ability to withstand high temperatures, resist oxidation, and provide effective lubrication under extreme conditions. Regular maintenance and lubrication practices ensure that the cylinder components continue to operate smoothly and reduce the effects of wear and friction.
7. Robust Construction:
– Hydraulic cylinders designed for harsh operating environments are built with robust construction techniques to withstand the rigors of such conditions. The cylinder barrels, rods, and other components are manufactured to meet strict quality and durability standards. Welded or bolted construction methods are employed to ensure the structural integrity of the cylinders. Reinforcements, such as flanges or tie rods, may be added to enhance the cylinder’s strength and resistance to external forces.
8. Environmental Protection:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be equipped with additional protective features to shield them from harsh operating environments. Protective covers, boots, or bellows can be used to prevent contaminants, debris, or moisture from entering the cylinder and compromising its performance. These protective measures help extend the service life of hydraulic cylinders in demanding conditions.
9. Compliance with Standards:
– Hydraulic cylinders manufactured for specific industries or applications often comply with industry standards or regulations related to operating temperature ranges, environmental conditions, or safety requirements. Compliance with these standards ensures that hydraulic cylinders are designed and tested to meet the specific demands of their intended operating environments.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders are designed to handle variations in temperature and harsh operating environments by incorporating suitable materials, thermal expansion considerations, heat dissipation mechanisms, corrosion-resistant components, specialized sealing systems, proper lubrication, robust construction techniques, protective features, and compliance with industry standards. These design considerations and features enable hydraulic cylinders to operate reliably and effectively in a wide range of demanding applications and environmental conditions.

Handling the Challenges of Minimizing Fluid Leaks and Contamination in Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders face challenges when it comes to minimizing fluid leaks and contamination, as these issues can impact the performance, reliability, and lifespan of the system. However, there are several measures and design considerations that help address these challenges effectively. Let’s explore how hydraulic cylinders handle the challenges of minimizing fluid leaks and contamination:
- Sealing Systems: Hydraulic cylinders employ advanced sealing systems to prevent fluid leaks. These systems typically include various types of seals, such as piston seals, rod seals, and wiper seals. The seals are designed to create a tight and reliable barrier between the moving components of the cylinder and the external environment, minimizing the risk of fluid leakage.
- Seal Material Selection: The choice of seal materials is crucial in minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. Hydraulic cylinder manufacturers carefully select seal materials that are compatible with the hydraulic fluid used and resistant to wear, abrasion, and chemical degradation. This ensures the longevity and effectiveness of the seals, reducing the likelihood of leaks or premature seal failure.
- Proper Installation and Maintenance: Ensuring proper installation and regular maintenance of hydraulic cylinders is essential for minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. During installation, attention should be given to proper alignment, torqueing of bolts, and adherence to recommended procedures. Regular maintenance includes inspecting seals, replacing worn-out components, and addressing any signs of leakage promptly. Proper maintenance practices help identify and rectify issues before they escalate and cause significant problems.
- Contamination Control: Hydraulic cylinders incorporate measures to control contamination and maintain fluid cleanliness. This includes the use of filtration systems, such as in-line filters, to remove particles and contaminants from the hydraulic fluid. Additionally, hydraulic reservoirs often have breathers and desiccant filters to prevent moisture and airborne contaminants from entering the system. By controlling contamination, hydraulic cylinders minimize the risk of damage to internal components and maintain optimal system performance.
- Environmental Protection: Hydraulic cylinders may be equipped with protective features to safeguard against external contaminants. For example, bellows or protective boots can be installed to shield the rod and seals from debris, dirt, or moisture present in the operating environment. These protective measures help extend the life of the seals and enhance the overall reliability of the hydraulic cylinder.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders employ sealing systems, appropriate seal materials, proper installation and maintenance practices, contamination control measures, and environmental protection features to handle the challenges of minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. By implementing these measures, manufacturers can ensure reliable and long-lasting hydraulic cylinder performance, minimize the risk of fluid leakage, and maintain the cleanliness of the hydraulic system.

What is a hydraulic cylinder and how does it function in various applications?
A hydraulic cylinder is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulic energy into linear force and motion. It plays a critical role in various applications where controlled and powerful linear motion is required. Hydraulic cylinders are commonly used in industries such as construction, manufacturing, agriculture, and transportation. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a hydraulic cylinder is and how it functions:
Definition and Components:
– A hydraulic cylinder consists of a cylindrical barrel, a piston, a piston rod, and various seals. The barrel is a hollow tube that houses the piston and allows for fluid flow. The piston divides the cylinder into two chambers: the rod side and the cap side. The piston rod extends from the piston and provides a connection point for external loads. Seals are used to prevent fluid leakage and maintain hydraulic pressure within the cylinder.
Function:
– The function of a hydraulic cylinder is to convert the pressure and flow of hydraulic fluid into linear force and motion. The hydraulic fluid, typically oil, is pressurized and directed into one of the chambers of the cylinder. As the fluid enters the chamber, it applies pressure on the piston, causing it to move in a linear direction. This linear motion of the piston is transferred to the piston rod, creating a pushing or pulling force.
Working Principle:
– The working principle of a hydraulic cylinder is based on Pascal’s law, which states that pressure exerted on a fluid in a confined space is transmitted equally in all directions. In a hydraulic cylinder, when hydraulic fluid is pumped into one side of the cylinder, it creates pressure on the piston. The pressure is transmitted through the fluid to the other side of the piston, resulting in a balanced force across the piston and piston rod. This force generates linear motion in the direction determined by the fluid input.
Applications:
– Hydraulic cylinders find extensive use in a wide range of applications due to their ability to generate high forces and precise control of linear motion. Some common applications include:
1. Construction Equipment: Hydraulic cylinders are used in excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes for lifting, pushing, and digging tasks.
2. Manufacturing Machinery: Hydraulic cylinders are employed in presses, machine tools, and material handling equipment for pressing, clamping, and lifting operations.
3. Agricultural Machinery: Hydraulic cylinders are used in tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems for tasks like steering, lifting, and controlling attachments.
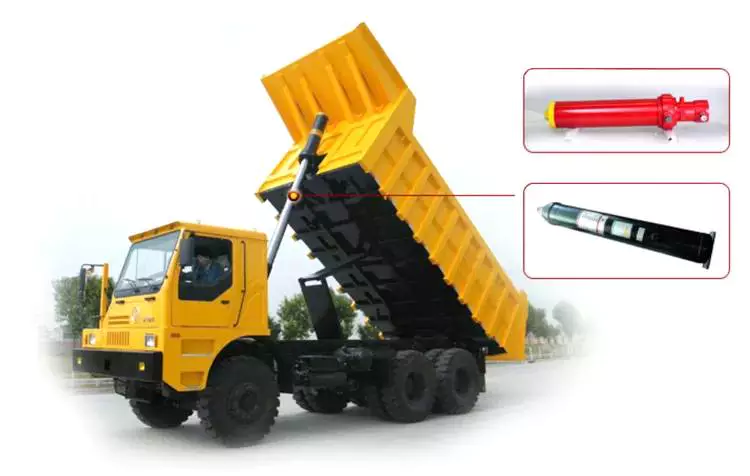
4. Transportation: Hydraulic cylinders are utilized in vehicles such as dump trucks, garbage trucks, and forklifts for tilting, lifting, and tipping operations.
5. Aerospace and Defense: Hydraulic cylinders are employed in aircraft landing gear, missile systems, and hydraulic actuators for control surfaces.
6. Marine and Offshore: Hydraulic cylinders are used in ship steering systems, cranes, and offshore drilling equipment for various lifting and positioning tasks.
In these applications, hydraulic cylinders offer advantages such as high force capability, precise control, compact size, and durability. They provide efficient and reliable linear motion, contributing to enhanced productivity and functionality in a wide range of industries.
Overall, hydraulic cylinders are integral components in various applications where controlled and powerful linear motion is required. Their ability to convert hydraulic energy into mechanical force makes them invaluable in numerous industries, enabling the operation of heavy machinery, precise positioning, and efficient load handling.


editor by CX 2023-11-20